5.3 Deriving the Three Principles of Relativity
The famous Michelson-Morley experiment in 1887 proved that light travels with the same speed regardless whether it was moving in the direction of the movement of the Earth or perpendicular to it. This unexpected null result initiated active research that eventually led to Special Relativity in 1905. The speed of light in vacuum is then considered the maximum speed which anything in the Universe can attain. Photons and other massless elementary particles propagate in vacuum at this terminal speed, regardless of the motion of the source or reference frame of the observer. However, even though this was confirmed by many experiments, there is yet no theoretical account that could explain the reasons behind this constancy and invariance of the speed of light.
Traveling faster than the speed of light would violate the causality principle, and accelerating to light speed or exceeding it would also violate certain energy conditions, but such justifications are actually the result of Einstein’s postulate and do not explain it in any philosophical sense. As we have reviewed in chapter III, later developments in elementary particles and field theories showed that particles move in the Higgs field and may interact with it. As a result of this interaction, particles acquire their mass. This may explain why some particles are heavier than others, and because they do not interact at all with the Higgs field, photons have no mass and therefore they move at the fastest possible speed. This, however, still does not explain why there is such a maximum speed in nature.
The Single Monad Model and its resulting postulate of the Duality of Time and continuous creation of space is the only model that provides a profound ontological reason of this cosmological speed limit, that is the speed of creation with regard to normal observers living the three-dimensional space.
Additionally, the invariance of physics laws, which is the second principle of Relativity, can also follow directly from the above postulate since we already showed that the instantaneous speed in the outer level of time is always zero, as described in Figure 5.1 above, which means that there is no any fundamental difference between objects moving at apparently different speeds since in reality they are always at rest at the actual time of measurement. Of course, if the reference frame is in acceleration, this has to be taken into account in the same manner as in General Relativity.
However, the most significant implication of the Duality of Time Postulate is that it appears to be the only way to explain the equivalence and transmutability between mass and energy (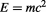 ). Einstein gave various heuristic arguments for this relation without ever being able to prove it in any theoretical way Hecht (2011), neither did anyone else.
). Einstein gave various heuristic arguments for this relation without ever being able to prove it in any theoretical way Hecht (2011), neither did anyone else.
Based on Doppler effect and Maxwell’s theory of radiation, the reasoning that Einstein gave in his 1905 original derivation Einstein (1905) was questioned by Planck Planck (1906) and shown to be faulty Ives (1952). In 1907, Einstein acknowledged the controversy over his derivation Einstein (1907), and in the following forty years, he produced more than half dozen proofs that all suffer from unjustified assumptions or approximations. He never succeeded in producing a valid general proof Ohanian (2009). In 1955 he wrote in a letter to Carl Seelig: “I had already previously found that Maxwell’s theory did not account for the micro-structure of radiation and could therefore have no general validity.” Capria (2005). In 1990, Rohrlich tried to apply the relativistic Doppler shift, but he had to introduce approximations in order to reach the final equation Rohrlich (1990). Various other attempts have been made in this regard but until now there is no exact derivation of this famous formula.
It will be shown in the following that the transmutability between mass and energy can only occur in the inner level of time, because it must involve motion at the speed of light that appears on the normal level of time as instantaneous, hence the fundamental laws of motion become inapplicable since they prohibit massive particles from moving at the speed of light. In the inner level of time, however, this would be the normal behavior because the metaphysical monads are still massless, and their continuous coupling and decoupling is what generates mass and energy on the inner and outer levels of time, respectively.
As we introduced above, that normal limited velocities of massive physical particles and objects are a result of the spatial and temporal superposition of the various dual-state velocities (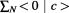 ) of their individual points or monads:
) of their individual points or monads: . This superposition occurs in the inward level of time where individually each point is massless and it is either at rest or moving at the speed of light, but collectively they have some non-zero inertial mass
. This superposition occurs in the inward level of time where individually each point is massless and it is either at rest or moving at the speed of light, but collectively they have some non-zero inertial mass , energy
, energy , and limited total velocity
, and limited total velocity .
.
We can now distinguish between four different cases:
1.When all points coincide at
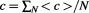
, the superposition state describes a light wave or a massless photon with energy
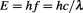
. 2.When all points coincide at
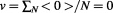
, the superposition state describes void, which is absolute nonexistence, not only an empty space which is termed as vacuum. 3.When some points are at
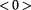
and other points are at
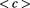
, the superposition state describes a particle with a mass

but the total vector velocity could still be zero, in which case the energy will be only the potential energy given by:
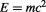
. 4.When some points are at
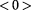
and other points are at
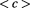
, and the total vector velocity is not zero, the superposition state describes a particle with a mass

, moving at an apparent speed

, and then its energy will be the kinetic energy plus the potential energy:
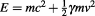
.
The difference between void and vacuum in this regard is that for void all points are in the ground state in all spatial dimensions, while vacuum describes the ground state inside the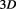 space, which is a flat
space, which is a flat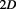 space, and so on: each level of space has its own ground state or vacuum, while void is the common ground state for all levels. This essential observation is the key to prove the Yang-Mill’s existence and mass gap.
space, and so on: each level of space has its own ground state or vacuum, while void is the common ground state for all levels. This essential observation is the key to prove the Yang-Mill’s existence and mass gap.
As demonstrated in Figure 5.1, one of the striking conclusions of the sequential re-creation in the inner level of time is the fact that it conceives of only two primordial states: vacuum and void, whose spatial and temporal superposition is producing the multiplicity of intermediary states that appear in the cosmos as matter particles. Vacuum, or empty space, is the continuous existence in the inner level of time, and void is the discrete existence in the outer level. These two extreme states can be conceived as abstract forms but only a relative superposition of them can ever be observed or measured as relative events in space-time, or inner-outer time that is the complex-time that will be discussed further in the following section 2.
For normal observers who are habitually living (as discrete instances) in the outer time, the continuous existence of vacuum appears moving at the terminal speed (of light) since it does not suffer the inertia that is experienced by massive particles and objects as they advance in the outer time. This inertia is the resistance that results from interrupting the continuous creation in the inner time in order to appear as discrete instances in the outer time. That is why the outer time is imaginary with relation to the inner time that is the real flow of creation.
Therefore, this dynamic and complex nature of time is the fundamental fact that underlines the emergence of dimensions. In other words: vacuum is the continuous and infinite existence which forms the inner real part of time, and whenever this existence is interrupted it makes a new dimension that appears as a discrete instance on the outer imaginary level which is then described as void since it does not last for more than one instance, before it is re-created again in a new state that may resemble the previous perished states.
This means that in the real flow of time in which space and matter are always being re-created, the individual geometrical points can either be at rest (in the outer/imaginary time) or moving at the speed of light (in the inner/real time), while the apparent limited velocities of compound particles and objects (in the complex time, which forms the physical dimensions of our space-time) are the temporal average of this spatial combination that may also dynamically change as they are progressing over the outward ordinary time direction.
Consequently, there is no gradual motion in the common sense that the object leaves its place to occupy new adjacent places, but it is successively re-created in those new places, i.e. motion occurs as a result of discrete change and not infinitesimal transmutation, so the observed objects are always at rest in the different positions that they appear in, as described in Figure 5.1. This is the same conclusion of the Moving Arrow argument in Zeno’s paradox, which Bertrand Russell described as: “It is never moving, but in some miraculous way the change of position has to occur between the instants, that is to say, not at any time whatever.” Salmon (2001).
Therefore, the Universe is always coming to be in “zero time” (on the outward level), and its geometrical points are sequentially fluctuating between existence and nonexistence (or vacuum and void), which means that the actual instantaneous speed of each point in space can only change from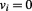 to
to , and vice versa.
, and vice versa.
This instantaneous abrupt change of speed does not contradict the laws of physics, because it is occuring sequentially in the inner levels of time before the physical objects are formed.
This fluctuation is the usual process that is encountered by the photons of light and other massless particles on the normal outward level of time. Hence, this model of continuous creation is extending this process onto all other massive particles and objects, but on the inner level of time where each point is still massless because it is metaphysical, while “space” and “mass” and other physical properties are actually generated from the temporal coupling and decoupling, or entanglement, of these geometrical points, which is exhibited only on the outward level of time.
Accordingly, normal limited velocities of massive physical particles and objects are a result of the spatial and temporal superposition of the various dual-states velocities of their individual points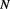 :
:
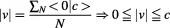
(5.3)
Individually, each point is massless and it is either at rest or moving at the speed of light, but collectively they have some non-zero inertial mass , energy
, energy , and limited total apparent velocity
, and limited total apparent velocity .
.
This means that all frames are effectively at rest in the normal (imaginary) level of time, and there is no difference between inertial and non-inertial frames, thus there is even no need to introduce the second principle of Special Relativity (which says that the laws of physics are invariant between inertial frames) neither the equivalence principle that lead to General Relativity.
These two principles, which are necessary to derive Lorentz boost and Einstein’s field equations, will follow directly from the complex-time geometry as it will be shown in sections 3.2 and 3.5 below.
Furthermore, it will be shown in section 3.3 that this essential fact that results from the genuinely complex nature of time is the only way that allows exact mathematical derivation of the mass-energy equivalence relation (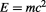 ) directly from the fundamental classical principles.
) directly from the fundamental classical principles.
In this way, the Duality of Time Postulate could explain at once all the three principles of Relativity and transform it into full Quantum Field Theory because it is now based on discrete instances of dynamic space, without any background. Additionally, the other fundamental forces could now be interpreted in terms of this new complex-time geometry, but in lower dimensions: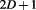 ,
,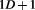 , and
, and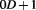 , while gravity is in
, while gravity is in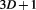 , as we shall describe in section 4.
, as we shall describe in section 4.