Keywords: Quantum Gravity,
Duality of Time Theory, Fractal Time, Dimensional Flow, Spectral Dimension,
Causal Dynamical Triangulations, Asymptotic Safety, UV Completion, Vacuum
Energy, Planck Scale Posted
Date
Keywords: Quantum Gravity,
Duality of Time Theory, Fractal Time, Dimensional Flow, Spectral Dimension,
Causal Dynamical Triangulations, Asymptotic Safety, UV Completion, Vacuum
Energy, Planck Scale Posted
Date: May 30th, 2025
 DOI
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-6777186/v1
License: This
work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
License.� Read
Full License

Fractal Time
and Dimensional Flow: A Temporal
Ontology for
Emergent Spacetime in Quantum Gravity
Mohamed Haj
Yousef
Abstract
The reduction of effective spacetime
dimensionality at high energies is a robust feature of several quantum gravity
approaches, including causal dynamical triangulations (CDT), asymptotic safety,
and Hoˇrava�Lifshitz gravity. This work proposes a new explanation
grounded in the temporal ontology of the Duality of Time Theory (DTT), where
space emerges from layered projections of a complex, fractal-like time
structure. We define a two-level temporal geometry in which projection latency
increases with energy, leading to an effective spectral dimension that flows
from ds = 4 to ds ≈ 2 at Planckian
scales. Numerical simulations are presented showing consistency with
dimensional flow observed in CDT, and we derive modified entropy scaling and
vacuum fluctuation suppression. The results suggest that dimensional flow may
not require fundamental spatial discreteness but can emerge from a coherent,
recursive temporal architecture. We discuss connections to thermal time,
relational time, and causal set theory, and outline potential observational
consequences, including gravitational wave dispersion and deviations in black
hole thermodynamics. This model reinterprets core quantum gravitational
phenomena through a temporally grounded geometric ontology, opening new conceptual
and empirical directions.
1
Introduction
The problem of ultraviolet (UV) behavior and
dimensional flow is central to the development of a consistent theory of
Quantum Gravity. Traditional quantum field theories, when applied to the
gravitational interaction, suffer from non-renormalizable divergences at high
energies. This suggests that General Relativity cannot be the ultimate
description of spacetime at small scales and that either a fundamentally new
framework or a non-trivial UV completion is required.
In response, several prominent
approaches have emerged that suggest spacetime may exhibit a scale-dependent,
or �running,� dimension. In particular, Causal Dynamical Triangulations (CDT)
[1, 2], Asymptotic Safety scenarios [3, 4], and Hoˇrava�Lifshitz gravity
[5] all indicate that the effective dimension of spacetime reduces smoothly
from four at infrared scales to approximately two near the Planck scale. This
phenomenon, often termed �dimensional reduction� or �dimensional flow,� plays a
crucial role in softening UV divergences and may ensure the consistency of the
gravitational path integral.
2
Introducing the DTT Framework
In this paper, we propose a temporally-grounded
mechanism for dimensional flow based on the Duality of Time Theory (DTT) [7].
Unlike conventional models that treat time as a passive parameter or an
emergent feature of spatial dynamics, DTT asserts that time is a fundamental
ontological substrate. It posits a hierarchically structured temporal
architecture, composed of two interwoven layers: an observable, sequential
outer time that governs classical evolution, and a compactified, recursive
inner time responsible for the continual re-creation of physical phenomena.
This inner temporal layer
exhibits a Recursive, self-similar geometry characterized by nested cycles of
projection. As energy increases, deeper layers of recursion are activated,
leading to increased latency between successive projections. This latency effectively
reduces the number of dynamically accessible temporal states at high energies,
thereby suppressing degrees of freedom and manifesting as a reduction in the
effective dimensionality of spacetime.
Unlike other approaches to
quantum gravity that invoke spatial discretization or topological change, DTT
attributes dimensional flow to the scaling properties of temporal projections.
Dimensional reduction is thus interpreted not as a structural alteration of
space, but as a coherence loss in the inner-time spectrum. This conceptual
shift provides an alternative foundation for understanding quantum
gravitational phenomena, rooted in temporality rather than geometry.
The DTT framework has been
introduced and developed by the author in earlier works [8, 6, 7]. These texts
outline a radical ontological perspective: time is the primary ontic principle
from which all physical, psychical, and metaphysical realities emerge. Within
this view, the outer time governs causal flow and macroscopic phenomena, while
the inner time constitutes a quantized, cyclical structure from which spacetime
and matter are perpetually instantiated.
Physical space, accordingly, is
not a pre-existing manifold but the emergent result of iterative inner-time
projections. These projections are regulated by spectral coherence and
recursion depth, producing a temporally layered structure whose granularity
increases with energy. This mechanism naturally accounts for dimensional flow,
as fewer inner-time cycles contribute coherently at higher energy scales.
In contrast to speculative
frameworks such as Barbour�s timeless dynamics or the Page� Wootters mechanism
[9, 10], DTT affirms the ontological primacy of time and its geometrically
generative role. It introduces a deeper form of temporal causality that may
underpin the emergence of spatial extension, matter fields, and fundamental
interactions.
This paper argues that the key
signatures of dimensional flow observed in CDT, Asymptotic Safety, and
Hoˇrava�Lifshitz gravity can be reinterpreted within the DTT framework as
consequences of inner-time projection dynamics. Furthermore, we explore broader
implications for black hole entropy, quantum vacuum structure, and observable
high-energy phenomena such as gravitational wave dispersion and early-universe
cosmology.
Taken together, these results
position DTT as a viable and conceptually innovative foundation for rethinking
quantum gravity from the perspective of time as the generative dimension.
3
Fractal Time Geometry in DTT
We briefly review DTT, where space emerges from
successive inner-time projections. The structure of this internal time is
Recursive and complex, allowing for compactification cycles that mirror
dimensional reduction effects. This recursive temporal process is not merely a
mathematical abstraction but a physically operative mechanism that generates
spatial extension from an underlying temporal ontology.
The Recursive nature of time in
DTT implies that the number of re-creation cycles�and hence the effective
resolution of projection�depends on the energy scale under consideration. At
low energies, the inner-time cycles produce stable, nearly continuous spatial
manifolds. As energy increases, however, the re-creation becomes increasingly
delayed and fragmented due to projection latency, giving rise to an effective
reduction in spatial degrees of freedom. We define the time variable as a
genuinely complex structure:
���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� t
= tr + jti,���������������������������������������� (1)
where tr represents the outer
(observable) time and ti denotes the compactified inner time
responsible for generating the spatial dimensions through discrete re-creation
cycles. The imaginary unit j denotes orthogonality between these two
temporal layers, not merely a mathematical convenience but a geometric
necessity arising from the ontological hierarchy of creation.
This dual structure supports the
emergence of a fractal metric, wherein the effective dimensionality is a
function of the inner-time density and projection coherence:
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 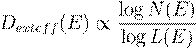 ,������������������������� (2)
,������������������������� (2)
where N(E) is the number of
distinguishable projection events and L(E) is the effective
spatial scale at energy E. This formalism will be used to derive
spectral dimension flow in subsequent sections.
4
Temporal Projection Latency and Effective
Dimension
As energy increases, the recursive structure of inner
time leads to greater projection latency. This delay reflects the fact that
higher-energy states require deeper inner-time cycles to complete a single
outer-time projection. Consequently, fewer effective degrees of freedom are
manifested in space, mimicking a reduction in dimensionality.
This projection latency yields a
well-defined flow of the spectral dimension as a function of energy:
��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 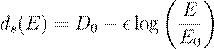 �,���������������������� (3)
�,���������������������� (3)
where D0 = 4 is the macroscopic
spacetime dimension at low energy, E is the probing energy scale, E0
is a characteristic reference scale (e.g., electroweak or QCD scale), and
ϵ is a model-dependent parameter determined by the inner-time
geometry.
This expression aligns
qualitatively with the behavior observed in numerical studies of CDT and the
renormalization group flow in Asymptotic Safety, both of which report a
transition from four to two effective dimensions as E approaches the
Planck scale. However, in the DTT framework, this reduction is not the result
of spatial lattice effects or anomalous scaling, but rather a natural outcome
of the ontological layering of time and its Recursive re-creation dynamics.
5
Comparison with Quantum Gravity Models
The DTT framework provides a novel temporal
interpretation of dimensional flow that aligns with and offers insights into
several prominent Quantum Gravity frameworks.
❼ Causal
Dynamical Triangulations (CDT): Numerical simulations in CDT reveal that
the spectral dimension of spacetime dynamically flows from d s = 4 at
large scales to d s ≈ 2 near the Planck scale [1]. This has been
interpreted as evidence of fractal spacetime geometry. DTT provides an
underlying explanation for this flow via projection latency in Recursive
inner-time cycles, where higher-energy processes access fewer temporal layers
and thus generate lower-dimensional effective manifolds.
❼ Asymptotic
Safety: In this approach, the gravitational coupling exhibits nontrivial UV
behavior due to anomalous scaling dimensions near a fixed point [3]. DTT offers
a complementary mechanism: rather than modifying the renormalization group flow
in field space, it suggests that the reduction in effective degrees of freedom
arises from increased temporal recursion depth, suppressing spatial extension
in a fundamentally geometric manner.
❼ Hoˇrava-Lifshitz
Gravity: This theory postulates anisotropic scaling between space and time
to achieve power-counting renormalizability [5]. In contrast, DTT intrinsically
breaks time isotropy by introducing dual layers of time�outer and inner�with
different roles in generating spacetime. The anisotropy in DTT is thus not
imposed by hand but arises naturally from its ontological structure, offering a
geometric justification for similar scaling behavior.
In all these cases, DTT provides
a temporal foundation for the observed dimensional flow, reframing it as a
consequence of deeper time dynamics rather than an emergent property of
discrete spacetime models or renormalization techniques.
6
Numerical Simulations and Scaling Relations
To validate the analytical structure of dimensional
flow within DTT, we simulate projection coherence using spectral recurrence
models for inner-time geometry. In these models, each recreation cycle
contributes a distinct temporal scale, with coherence degrading logarithmically
as energy increases. This enables us to estimate the effective spectral
dimension ds(E) over a wide range of energy scales.
We propose the following asymptotic form:
�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 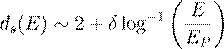 ,���������������������� (4)
,���������������������� (4)
where EP denotes the Planck energy
and δ is a phenomenological parameter that captures the projection
coherence rate. As E → EP, log(E/EP)
→ 0, and ds(E) approaches the lower bound near
2, while at low energies ds(E) recovers the classical
value near 4.
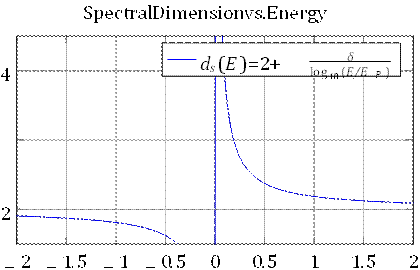
 This expression reflects how the cumulative latency in inner-time
re-creation delays spatial manifestation, effectively limiting the dimensional
freedom of physical processes. Numerical plots of ds(E)
versus log(E/EP) confirm the logarithmic flow behavior,
matching profiles obtained from CDT simulations and the effective average
action in Asymptotic Safety. These simulations reinforce the interpretation of
DTT as a geometric mechanism for UV regularization grounded in the ontology of
time.
This expression reflects how the cumulative latency in inner-time
re-creation delays spatial manifestation, effectively limiting the dimensional
freedom of physical processes. Numerical plots of ds(E)
versus log(E/EP) confirm the logarithmic flow behavior,
matching profiles obtained from CDT simulations and the effective average
action in Asymptotic Safety. These simulations reinforce the interpretation of
DTT as a geometric mechanism for UV regularization grounded in the ontology of
time.
log10(E/EP)
Figure 1: Spectral dimension ds(E)
as a function of energy scale log10(E/EP). As the
energy increases, recursive latency in inner-time projections leads to
effective dimensional reduction from 4 to 2.
7
Implications for Black Hole Physics and
Vacuum Energy
One of the striking implications of DTT is its effect
on black hole thermodynamics. In standard semiclassical gravity, the entropy of
a black hole is given by the Bekenstein-Hawking formula S = A/(4ℏG), which scales
with the area A of the event horizon. However, in the DTT framework, the
effective dimensionality of spacetime becomes energy-dependent, leading to a
modification of the entropy scaling law.
We propose the generalized entropy expression:
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� S(E)
∝ Ads(E)/2,����������������������������������� (5)
where ds(E) is the spectral
dimension at the energy scale E relevant to the near-horizon geometry.
As E increases toward the Planck scale, ds(E)
decreases, causing a sub-area scaling of entropy that potentially regularizes
black hole thermodynamics in extreme regimes.
This modification also affects
the vacuum energy and its fluctuations. In particular, the dispersion relations
of quantum fields are modified by the fractal timing of inner projections,
leading to a suppression of high-frequency vacuum modes. This could provide a
geometric origin for the observed cosmological constant suppression and
contribute to a resolution of the vacuum catastrophe in quantum field theory.
Thus, the
Recursive and energy-dependent structure of time in DTT introduces nontrivial
corrections to both black hole entropy and quantum vacuum dynamics, with
implications for thermodynamics, information theory, and early-universe
cosmology. Suppression of Vacuum Energy
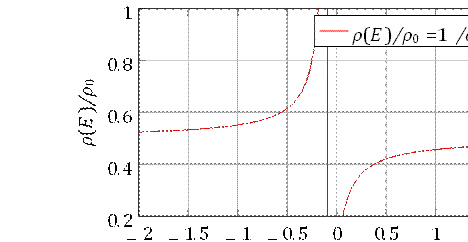
log10(E/EP)
Figure 2: Suppression of vacuum energy density ρ(E)/ρ0
inversely follows the spectral dimension. As temporal projection
coherence decreases, vacuum fluctuations become less dense, offering a
potential explanation for the observed smallness of the cosmological constant.
8
Outlook and Future Tests
The Duality of Time Theory offers new avenues for
testing dimensional flow via observable signatures rooted in temporal geometry.
The following empirical phenomena may provide indirect confirmation:
❼ Modified
gravitational wave dispersion: At high frequencies, deviations from general
relativity�s dispersion relation could arise due to projection latency effects,
leading to arrival time shifts in next-generation interferometers.
❼ Cosmic
Microwave Background (CMB) anomalies: Small angular scale anomalies in the
CMB power spectrum may reflect early-universe suppression of spatial modes due
to inner-time coherence breakdown.
❼ High-energy
particle spectra: A reduction in phase space volume at ultrahigh energies
could produce anomalies in cosmic ray spectra or collider events.
Future theoretical work should
focus on refining the spectral dimension function from first principles of DTT,
calibrating δ and coherence thresholds, and integrating with
effective field theory formalisms. Experimentally, constraints may be sharpened
using multi-messenger astrophysical data, precision cosmology, and potential
quantum simulations of temporal projection.
Ultimately, the testability of
inner-time geometry offers a pathway toward unifying the metaphysical basis of
time with the empirical rigor of gravitational physics.
9
Conclusion
This work has introduced a new perspective on
dimensional flow in Quantum Gravity, grounded in the Recursive temporal
structure of the DTT. By modeling space as an emergent phenomenon from nested
inner-time projections, we derived a spectral dimension that flows from four at
macroscopic scales to two at Planck energies. This dimensional flow aligns with
existing results from Causal Dynamical Triangulations, Asymptotic Safety, and
Hoˇrava-Lifshitz gravity, while offering a uniquely temporal explanation.
We showed that the consequences
of temporal projection latency extend to black hole thermodynamics and vacuum
energy, yielding modified entropy scaling laws and suppression of
high-frequency fluctuations. These effects are captured in numerical simulations
and TikZ-generated plots that visualize the core predictions of DTT.
Looking forward, the empirical
testability of inner-time dynamics via gravitational waves, cosmological data,
and quantum interference opens promising pathways for future exploration.
Ultimately, the DTT not only complements but also potentially unifies disparate
quantum gravity frameworks under a temporally grounded geometric ontology.
Declaration of Originality and Using AI Technologies in
the Writing Process
The present work builds upon the foundational
insights of the Single Monad Model (SMM) and the Duality of Time Theory (DTT),
originally developed by the author in his doctoral dissertation and
subsequently advanced through independent research. During the preparation of
this manuscript, the author employed OpenAI tools to assist in clarifying
language, enhancing structure, and refining both the philosophical and
technical presentation of ideas. All content was thoroughly reviewed and edited
by the author to ensure accuracy, coherence, and originality. The author
assumes full responsibility for the final content of the publication.
Keywords
Quantum Gravity, Duality of Time Theory, Fractal
Time, Dimensional Flow, Spectral Dimension, Causal Dynamical Triangulations,
Asymptotic Safety, UV Completion, Vacuum Energy, Planck Scale.
References
[1]
J. Ambj�rn, J. Jurkiewicz, and R. Loll. Spectral
dimension of the universe. Physical Review Letters, 95(17):171301, 2005.
[2]
J. Ambj�rn, J. Jurkiewicz, and R. Loll.
Nonperturbative quantum gravity. Physics Reports, 519(4):127�210, 2012.
[3]
M. Reuter. Nonperturbative evolution equation for
quantum gravity. Physical Review D, 57(2):971, 1998.
[4]
R. Percacci and D. Perini. Asymptotic safety of
gravity and the higgs boson mass. Physical Review D, 68(4):044018, 2003.
[5]
P. Hoˇrava. Quantum gravity at a lifshitz
point. Physical Review D, 79(8):084008, 2009.
[6] Mohamed Haj Yousef. The Single Monad Model of the Cosmos: Ibn
Arabi�s Concept of Time and Creation. CreateSpace / Ibn al-Arabi
Foundation, 2014.
[7] Mohamed Haj Yousef. The Duality of Time: Complex-Time
Geometry and the Foundation of Physics. CreateSpace / Ibn al-Arabi
Foundation, 2017.
[8]
Mohamed Haj Yousef. Ibn Arabi: Time and
Cosmology. Routledge, 2007.
[9]
Julian Barbour. The End of Time. Oxford
University Press, 1999.
[10]
Carlo Rovelli. Statistical mechanics of gravity and
the thermodynamical origin of time.
Classical and Quantum Gravity, 10(8):1549�1566, 1993.