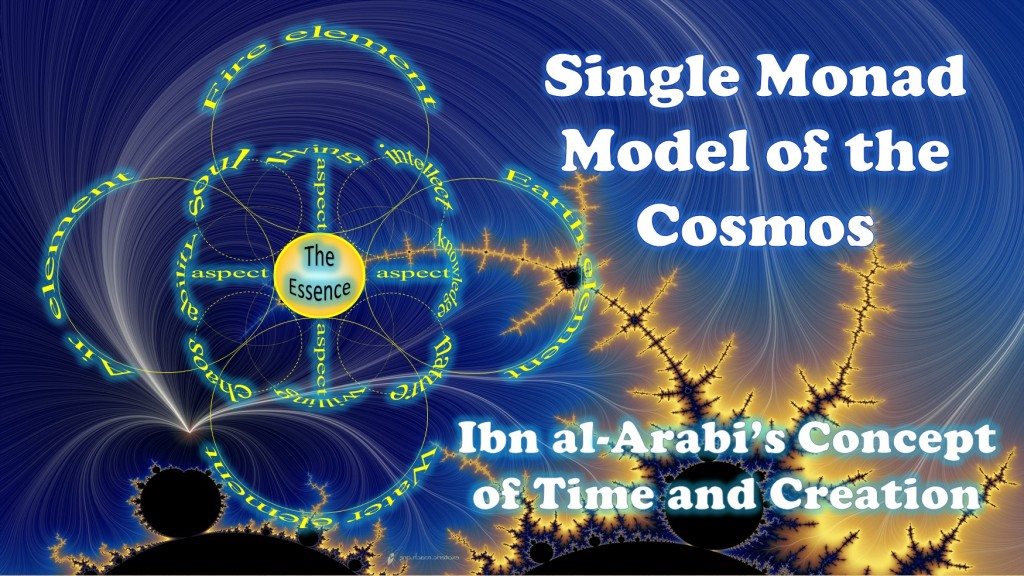
6.9.1 Exclusion Principle
The exclusion principle is one of the fundamental observation in quantum physics, which was introduced in 1924, to resolve the inconsistencies between the observed molecular spectra and the predictions of Quantum Mechanics, as we have explained in chapter III. This principle states that “there cannot exist an atom in such a quantum state that two electrons within [it] have the same set of quantum numbers.” Shortly after that the property of spin was observed in the famous Stern-Gerlach experiment. From the calculations performed by Schroedinger for the energy levels of hydrogen, the distributions of probabilities for electron positions and locations are related to four quantum properties: orbital, shape, inclination, and spin, each of which has a quantum number and they collectively describe the quantum state of the electron.
So the Pauli exclusion principle demands that no two electrons within an atom may have the same values of all four quantum numbers, which gives rise to the different possible arrangements of the orbitals that lead to the organization of the periodic table of chemical elements.
This also lead to the main field of quantum statistics, that includes Fermi-Dirac and Bose-Einstein distributions of particles over energy states. The first describes particles that obey Pauli exclusion principle, thus called fermions, having spin-half, and the latter describes particles that do not obey this principle, thus called bosons, having integer spins.
This exclusion principle resulted from the observations of atomic spectra, supported later by the various theoretical and experimental studies on spin and magnetic properties of moving charges, but there is no fundamental explanation as to why these various discrete states are imposed and can not be duplicated together in the same atom!
According to the Duality of Time, all particles and objects are sequential manifestations of the Single Monad, that can either be in the inner level that constitutes the real dimensions of space, or the outer level that is the imaginary dimension of time. Therefore, bosons are “space particle” while fermions are “time particles”, not the opposite, because the latter are created internally at the speed of light, like everything else, but they move through the outer imaginary time, at a limited velocity that can not reach the speed of light, while bosons move in space and time together at the speed of light. Therefore, bosons are described by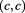 while fermions are described by
while fermions are described by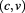 , and the reason why we have various generations of each type is due to the number of dimensions. Here, however, there are many details which may contradict the established, but incomplete, conclusions of the Standard Model, although these contradictions can be resolved easily but this requires detailed analysis beyond this book.
, and the reason why we have various generations of each type is due to the number of dimensions. Here, however, there are many details which may contradict the established, but incomplete, conclusions of the Standard Model, although these contradictions can be resolved easily but this requires detailed analysis beyond this book.
Nevertheless, we can say that in principle we should have seven degrees of spin, and these are the same seven heavens, or celestial orbs, that we described in chapter VII (section 2.3); each corresponding to one degree of freedom, or one level of time, and each two opposite consecutive time directions make up one dimension of space, which is why two complementary fermions, such as the electron and the positron, each of spin half, can annihilate into one boson of spin one, and the opposite is also possible.
However, the most fundamental reason behind the exclusion principle is the reality of oneness; that in the real flow of time only one real entity exist, at any given discrete instance, that is the Single Monad that is always moving at the speed of light; because with regard to itself it is always in the state of being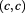 , which forms the
, which forms the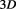 flat space for some hypothetical external observer, as we described in section 8.
flat space for some hypothetical external observer, as we described in section 8.
If the world remained in this state of oneness, or unity, it would have been described by absolute Bose-Einstein statistics, which means that all its (constant) entities are non-interacting indistinguishable “particles” that occupy the same state, such as what happens in an ideal super-fluid, which is the state of “water” from which Allah made everything living, or moving, as we will see in chapter VII (section 1.4).
The creation of the world happened as a result of splitting this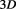 ideal space, which introduced the outer level of time in which fermions started to move and take various different states. The reason why these states are discrete, and therefore no two particles can exist in exactly the same state, is because they exist in the imaginary time, which is the very fact that caused them to become multiple. If remained in the real flow of time, all hypothetical particles become indistinguishable One or whole, so those which turns out to the imaginary time, by being multiplied by the imaginary number unit
ideal space, which introduced the outer level of time in which fermions started to move and take various different states. The reason why these states are discrete, and therefore no two particles can exist in exactly the same state, is because they exist in the imaginary time, which is the very fact that caused them to become multiple. If remained in the real flow of time, all hypothetical particles become indistinguishable One or whole, so those which turns out to the imaginary time, by being multiplied by the imaginary number unit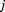 which produces an abrupt rotation by
which produces an abrupt rotation by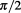 as we explained in chapter IV. This is exactly what gives them spin-half with relation to the observer who is necessarily in orthogonal time dimension, since that is what it means for them to be in imaginary time.
as we explained in chapter IV. This is exactly what gives them spin-half with relation to the observer who is necessarily in orthogonal time dimension, since that is what it means for them to be in imaginary time.
So since all fermions are kinetically moving in the outer time which is imaginary, they must exist in different states, because we are observing them from orthogonal direction(s), otherwise we would not see them many. In contrast to that, because bosons are in the real level of time with respect to the observer, they all appear in the same state even though they may be infinite.
The first case is like looking at the various points of the inner surface of a sphere surrounding the observer, so he or she has to move around, even by imagination, to distinguish between the different points, while the second case is like looking along a straight line which has an infinite number of points, but they are indistinguishable and they all are perceived as one.