5.3.5 Equivalence Principle
In moving from special to General Relativity, Einstein observed the equivalence between the gravitational force and the inertial force experienced by an observer in a non-inertial frame of reference. This is the same as the equivalence between active gravitational and passive inertial masses, which has been later accurately tested in many experiments, but there is not direct mathematical derivation apart from the famous spacecraft accelerator thought experiment which relies on induction. When Einstein combined this principle with the two principles of Special Relativity, he was able to predict the curved geometry of space-time, which is directly related to its contents of energy and momentum of matter and radiation, through a system of partial differential equations known as Einstein field equations.
We explained in section 3.3 above that an exact derivation of the mass-energy equivalence relation is not possible without postulating the Duality of Time, because it requires motion at the speed of light which is not possible on the physical level. It turned out also that this complex character of time is also required to obtain a direct derivation of the equivalence principle, which is in fact equivalent to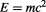 or
or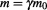 , because they are all a result of the fact that space and matter are being perpetually re-created in the inner time, i.e. converted between the particle state and wave state, and this is the only way that lead to granular and dynamic space-time without any background, as we explained in sections 2 and 2.2 above.
, because they are all a result of the fact that space and matter are being perpetually re-created in the inner time, i.e. converted between the particle state and wave state, and this is the only way that lead to granular and dynamic space-time without any background, as we explained in sections 2 and 2.2 above.
The representation of the complex momentum in Figure 5.5 that is based on the complex time frame as illustrated in Figure 5.1 indicates that the modulus of the complex momentum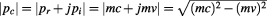 should be invariant between inertial and non-inertial frames alike, because effectively the object is always at rest in the outer level of time as we showed in section 2 above. This means that momentum is conserved even when velocity changes, i.e. as the object accelerates between non-inertial frames. Actually, without this exotic property of momentum it is not possible at all to obtain an exact derivation of
should be invariant between inertial and non-inertial frames alike, because effectively the object is always at rest in the outer level of time as we showed in section 2 above. This means that momentum is conserved even when velocity changes, i.e. as the object accelerates between non-inertial frames. Actually, without this exotic property of momentum it is not possible at all to obtain an exact derivation of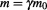 which is equivalent to
which is equivalent to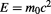 as we mentioned in section 3.3 above and in section 3.3.8. These experimentally verified equations are correct if and only if the total momentum
as we mentioned in section 3.3 above and in section 3.3.8. These experimentally verified equations are correct if and only if the total momentum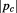 is always conserved. For example when the object accelerates from zero to
is always conserved. For example when the object accelerates from zero to , we get:
, we get:
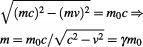
(5.28)
Furthermore, it is this exotic property that makes space-time itself dynamic and quantized without any background, because this requires that particles and objects are always at rest in their instantaneous locations, as Zeno indicated about two millenniums ago, as we explained in chapter II, since we explained in section 3 above that there is no real gradual motion but a discrete change without transmutation, see also: Haj Yousef (2014).
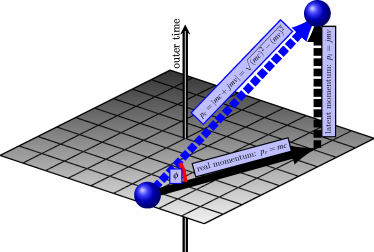
Figure 5.5: The complex-momentum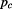 is combined from the real part that is the rest momentum in the inner time
is combined from the real part that is the rest momentum in the inner time , with the imaginary part that is the normal kinetic momentum
, with the imaginary part that is the normal kinetic momentum on the outer level of time, thus:
on the outer level of time, thus: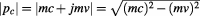 .
.
The invariance of momentum between non-inertial frames is conceivable despite the change in velocity, because it means that as the velocity increases, the gain in kinetic momentum (that is the imaginary part) is compensated by the increase in the effective mass:
(that is the imaginary part) is compensated by the increase in the effective mass: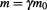 due to motion, which causes the real part
due to motion, which causes the real part also to increase, but since
also to increase, but since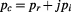 is hyperbolic, thus its modulus
is hyperbolic, thus its modulus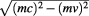 remains invariant.
remains invariant.
Therefore, in addition to the previous two methods in equations 5.9 and 5.10, and the relativistic energy-momentum relation in equation 5.27, the mass-energy equivalence relation: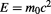 can now be deduced from equation 5.28 as it is shown in section 3.3.8 below, because, as we mentioned above, the equations:
can now be deduced from equation 5.28 as it is shown in section 3.3.8 below, because, as we mentioned above, the equations: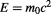 and
and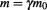 are equivalent, and the derivation of one of them leads to the other. Without the concept of genuinely imaginary time, this essential equation can not be derived.
are equivalent, and the derivation of one of them leads to the other. Without the concept of genuinely imaginary time, this essential equation can not be derived.
The absolute conservation of momentum can be easily concluded from Figure 5.3 simply by multiplying the velocity with mass on the inner and outer levels, but because of its importance we modified it here into Figure 5.5 and since this essential modification leads also to the mathematical derivation of the equivalence principle of General Relativity, which is currently only obtained by induction, from the famous spacecraft accelerator thought experiment.
This conservation of momentum under acceleration leads directly to the equivalence principle of General Relativity, because it means that the total (complex) force: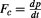 must have two components; one that is related to acceleration as
must have two components; one that is related to acceleration as changes, which is the imaginary part that is related to the outward time
changes, which is the imaginary part that is related to the outward time , and this is the accelerating force
, and this is the accelerating force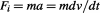 , while the other is related to the change in effective inertial mass
, while the other is related to the change in effective inertial mass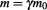 , or the energy
, or the energy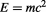 , which is manifested as the curvature of the geometry of space which is being re-created in the inner time
, which is manifested as the curvature of the geometry of space which is being re-created in the inner time , and this is the gravitational force
, and this is the gravitational force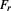 ; and these two components must be equivalent so that the total resulting complex momentum remains conserved. This also means that the inertial mass is itself the gravitational mass.
; and these two components must be equivalent so that the total resulting complex momentum remains conserved. This also means that the inertial mass is itself the gravitational mass.
We can then write:
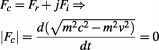
(5.29)
This gives the equivalence between the gravitational force and the pseudo-force experienced by an observer in a non-inertial frame. From this conservation of complex momentum we should be able to find the law of gravitation and the stress-energy-momentum tensor which leads to Einstein’s field equations of General Relativity. This important conclusion requires further investigation, but the most important issue is that this equivalence principle should apply to all fundamental forces and not only to gravity. This will be investigated further in chapters VI and VII.





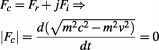 (5.29)
(5.29)